The java lang math ceil double a returns the smallest closest to negative infinity double value that is greater than or equal to the argument and is equal to a mathematical integer.
Math roof java.
If the argument is nan or an infinity or positive zero or negative zero then the result is the same as the argument.
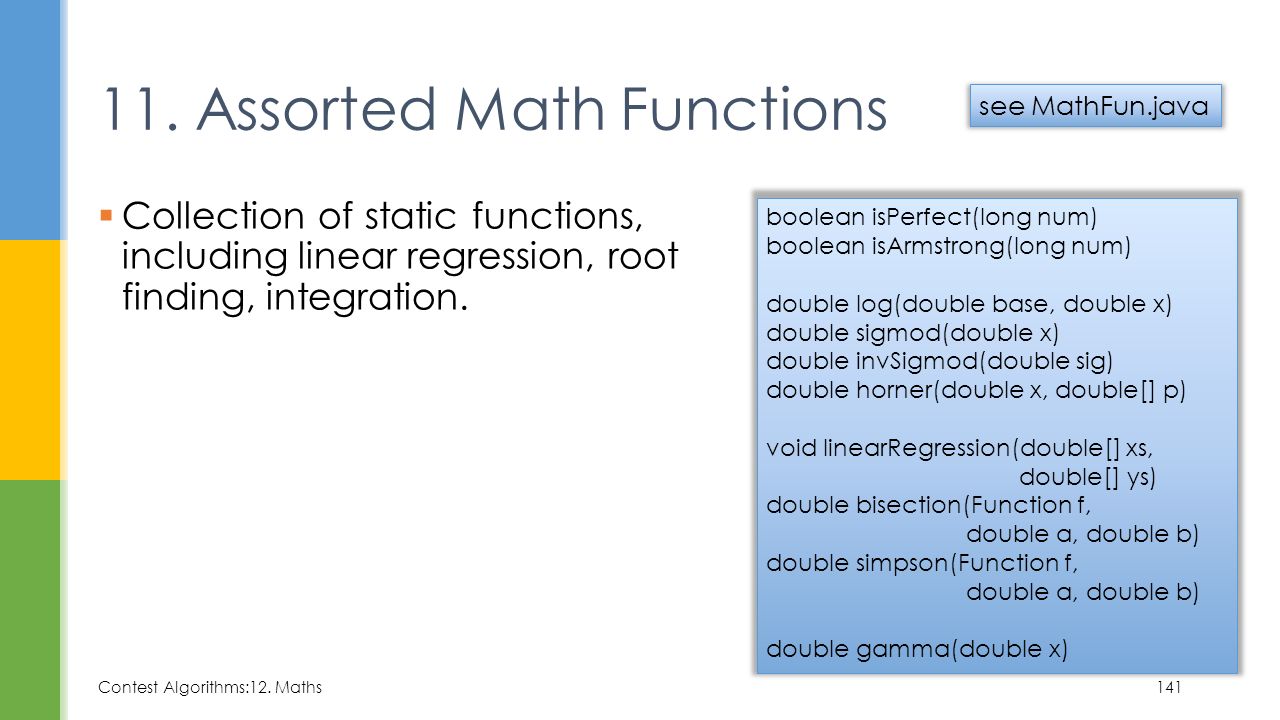
A let us have a look at the table below that shows us the basic methods and its description.
The class math contains methods for performing basic numeric operations such as the elementary exponential logarithm square root and trigonometric functions.
Java offers a wide variety of math functions to perform different tasks such as scientific calculations architecture designing structure designing building maps etc.
If the argument is nan or an infinity or positive zero or negative zero then the result is the same as the argument.
Math e having a value as 2 718281828459045.
In this document we are discussing several basic trigonometric logarithmic and angular math functions in detail with sample programs and examples.
The java lang math floor returns the double value that is less than or equal to the argument and is equal to the nearest mathematical integer.
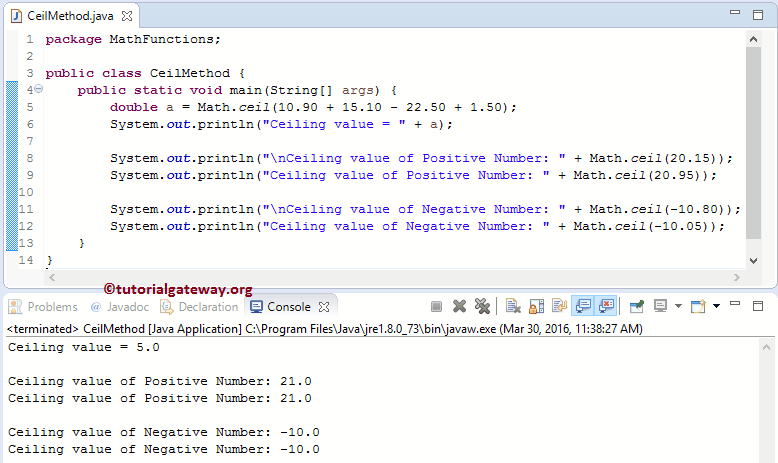
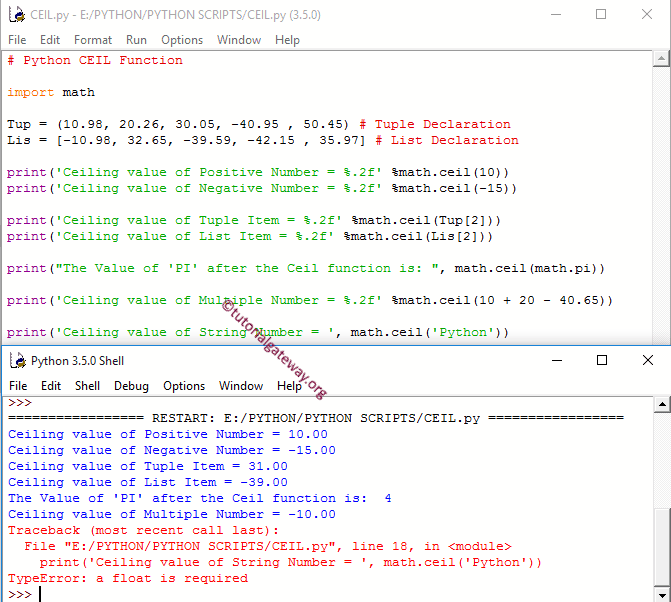
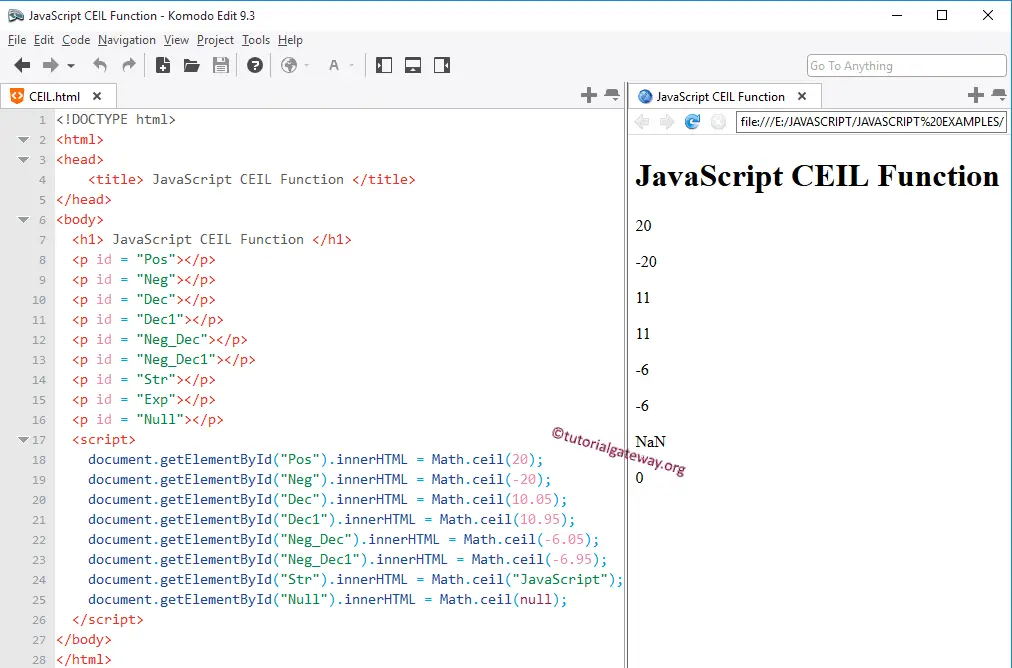
The java lang math ceil returns the double value that is greater than or equal to the argument and is equal to the nearest mathematical integer.
Unlike some of the numeric methods of class strictmath all implementations of the equivalent functions of class math are not defined to return the bit for bit same results.
This relaxation permits better performing implementations.
Hence the math class java provides these two constants as double fields.
Special cases if the argument value is already equal to a mathematical integer then the result is the same as the argument.
Well organized and easy to understand web building tutorials with lots of examples of how to use html css javascript sql php python bootstrap java and xml.
Java ceil method the method ceil gives the smallest integer that is greater than or equal to the argument.
The java lang math floor is used to find the largest integer value which is less than or equal to the argument and is equal to the mathematical integer of a double value.